List Two Types of Spinal Nerves and Describe Their Functions
For the most part the spinal nerves exit the vertebral canal through the intervertebral foramen below their corresponding vertebra. This plexus divides into nerves that carry sensory messages and control the abdominal and legs muscles.
Spinal nerves L1 to L4 combine to form the lumbar plexus.
. Dorsal and Ventral Roots. The trigeminal nerve V has sensory and somatic motor functions. Spinal nerves are involved in movement sensation and sweat secretion.
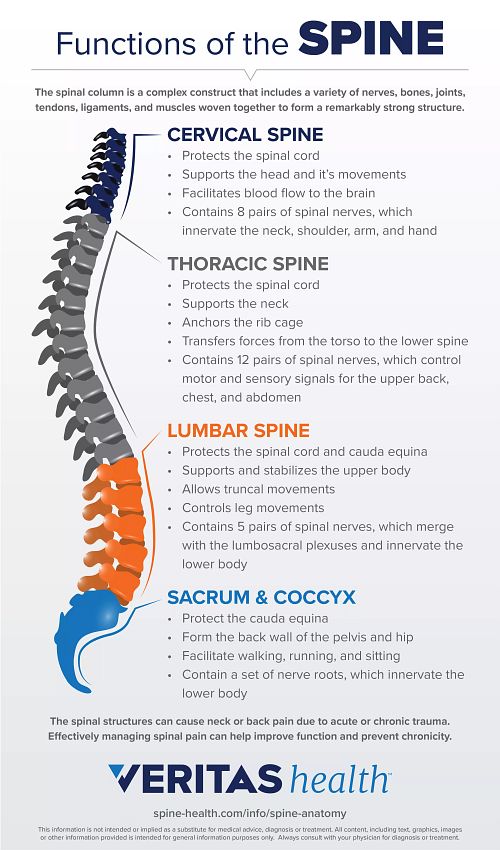
8 cervical 12 thoracic 5 lumbar 5 sacral and 1 coccygeal. Exercises can strengthen the core muscles that support the spine and. The first 4 cervical spinal nerves C1 through C4 split and recombine to produce a variety of nerves that subserve the neck and back of the head.
These are the sensory nerves motor nerves and mixed nerves. There are two main types. Functionally the PNS can be divided into the autonomic and somatic nervous systems.
This nerve controls movement of the muscles of the neck. This nerve is also known as nerve XI and arises from two roots namely the cranial and spinal bones. In humans there are 31 pairs.
The spinal accessory nerve provides function to the sternocleidomastoid muscle the upper back and the shoulder. Each pair connects the spinal cord with a specific region of the body. Both of these can be further subdivided.
Describe the function of two areas of the brain that you found interesting during the sheep brain dissection. There are three types of nerves in the human body which are classified based on their functions. Cranial and spinal nerves are the two components of the peripheral nervous system.
An Integrative Approach 2nd Edition Michael McKinley Dr. Chapter 72 Problem 3WDYL. Key parts of your spine include vertebrae bones disks nerves and the spinal cord.
These are the nerves that send messages to the brain or the spinal cord from the sense organs. The disks that cushion vertebrae may compress with age or injury leading to a herniated disk. The spine supports your body and helps you walk twist and move.
One composed of sensory fibres enters the spinal cord. Spinal nerves and cranial nerves. Any dysfunction of this cranial.
The former into sympathetic and parasympathetic arms and the latter into sensory and motor divisions. Label the four cerebral cortex lobes and describe some primary functions of each - frontal lobe parietal lobe 2. Textbook solution for Anatomy Physiology.
Along with these two types of nerves that arise from the brain and spinal cord the central nervous system communicates successfully with the rest of the. Which pick up and transmit messages from receptor cells to the spinal cord to the brain. Spinal nerves do not form dorsal and ventral roots.
Autonomic nervous system ANS - control of involuntary MOTOR nerve body functions ex heartbeat and digestion 2b. Read more about Nervous System Diseases. LAB 4 POST-LAB WORKSHEET 1.
Therefore depending on the originating place either brain or spinal cord of the nerves peripheral nervous system nerve cells can be classified into two categories namely cranial nerves and spinal nerves. The ventral primary ramus supplies structures on the limbs the skin along the lateral and ventral surfaces of the trunk and skeletal muscles except the deep back muncles Ventral root Function The rami branches along thoracic and lumbar spinal nerves that are associated with the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system DThe cauda equina forms because the. Spinal nerves L4 to S4 merge and then branch out into nerves that carry sensory messages and provide motor control to the muscles of the legs.
The PNS is built almost entirely from nerves. Provide for movement by innvating muscles or causing organs to function -SENSORY NERVES. The next lobe is the occipital lobe its function is to receive and perceive visual input.
The central nervous system or CNS is made up of the brain and spinal cord. List the two types of spinal nerves and describe their function -MOTOR NERVES. It has the greatest general sensory distribution of all the cranial nerves and is the only cranial nerve supplying sen-sory information to the brain from the skin of the face.
Somatic nerous system- Voluntary motor nerves 2c. Therefore there are 12 pairs of thoracic spinal nerves 5 pairs of lumbar spinal nerves 5 pairs of sacral spinal nerves and a coccygeal nerve. This nerve controls swallowing movements and helps in the movement of head and shoulders.
There are actually two parts of the Accessory Nerve which are the spinal and cranial divisions of which the cranial subdivision is disregarded. The cervical spinal nerves differ from this pattern. Spinal nerve in vertebrates any one of many paired peripheral nerves that arise from the spinal cord.
The peripheral nervous system or PNS is made up of the nerves in the rest of the body. Together with brain it forms the central nervous system which coordinates the functions of various organs of our body. This nerve facilitates the movement of the tongue and helps to talk swallowing etc.
Which types of spinal nerves were activated when the calipers were. These are enclosed in the form of a bundle like structures. Motor nerves control the movement and.
The fourth lobe is the temporal lobe this lobe has a role in the sensation of smell and hearing and is also important in memory. Cranial nerves form dorsal and ventral roots. The spinal cord has a crucial role to play in various functions of our body including the movement of our limbs and the transmission of sensory and motor nerve impulses to and from the brain.
Sensory information from the skin over the rest of the body is carried to the CNS by spinal nerves. Near the spinal cord each spinal nerve branches into two roots. Sensory nerves are involved with your senses such as smell hearing and touch.
Their functions are usually categorized as being either sensory or motor. In fact along with neurons they comprise the two types of cells in nervous tissue and are integral to the functioning of the CNS and PNS. We have step-by-step solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts.
C2 and C3 form many of the nerves of the neck and provides both sensory and motor control. Spine Structure and Function. The spinal nerve C1 suboccipital nerve provides motor innervation to muscles at the base of the skull.
These two lobes are separated by the central sulcus.
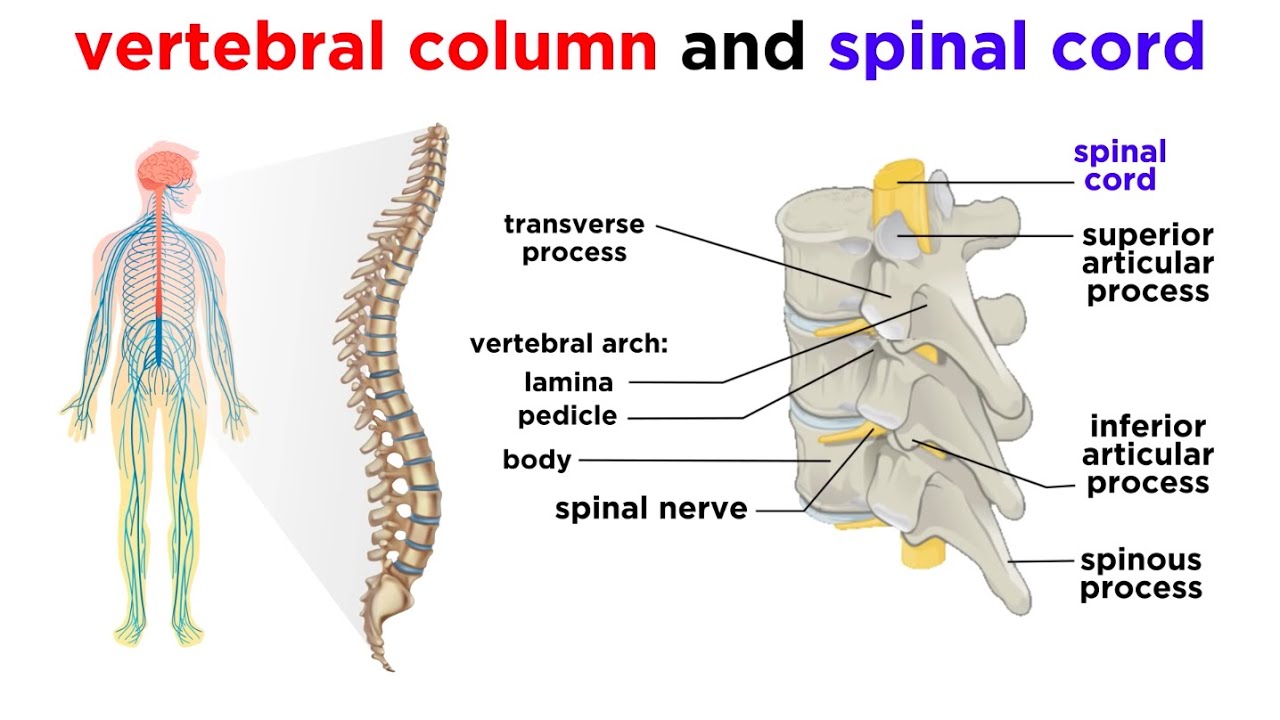
The Central Nervous System The Brain And Spinal Cord Youtube

13 3 Spinal And Cranial Nerves Anatomy Physiology
Difference Between Cranial And Spinal Nerves Definition Types Function

Spinal Nerve Definition Function Diagram Number Facts Britannica
/tingling-numbness-2549269_V2-69a8afe7b9a24e42a04e8325ebbcf537-3e324beb14e94ef4a5f26a1fc8274148.gif)
Spinal Nerves Anatomy Function And Treatment
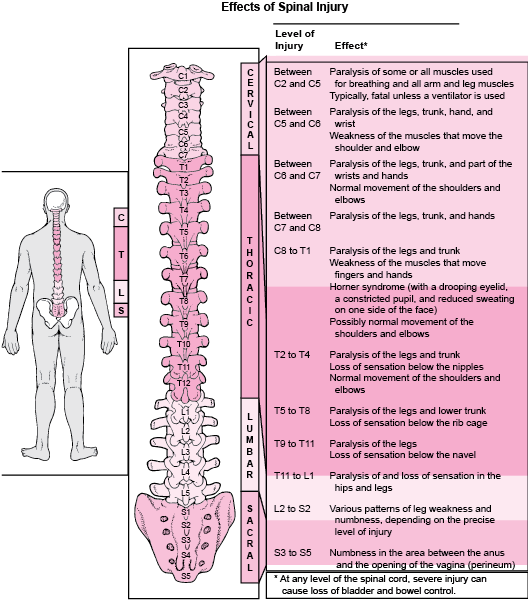
Overview Of Spinal Cord Disorders Brain Spinal Cord And Nerve Disorders Merck Manuals Consumer Version

12 6 Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerves Medicine Libretexts

Spinal Nerve Definition Function Diagram Number Facts Britannica
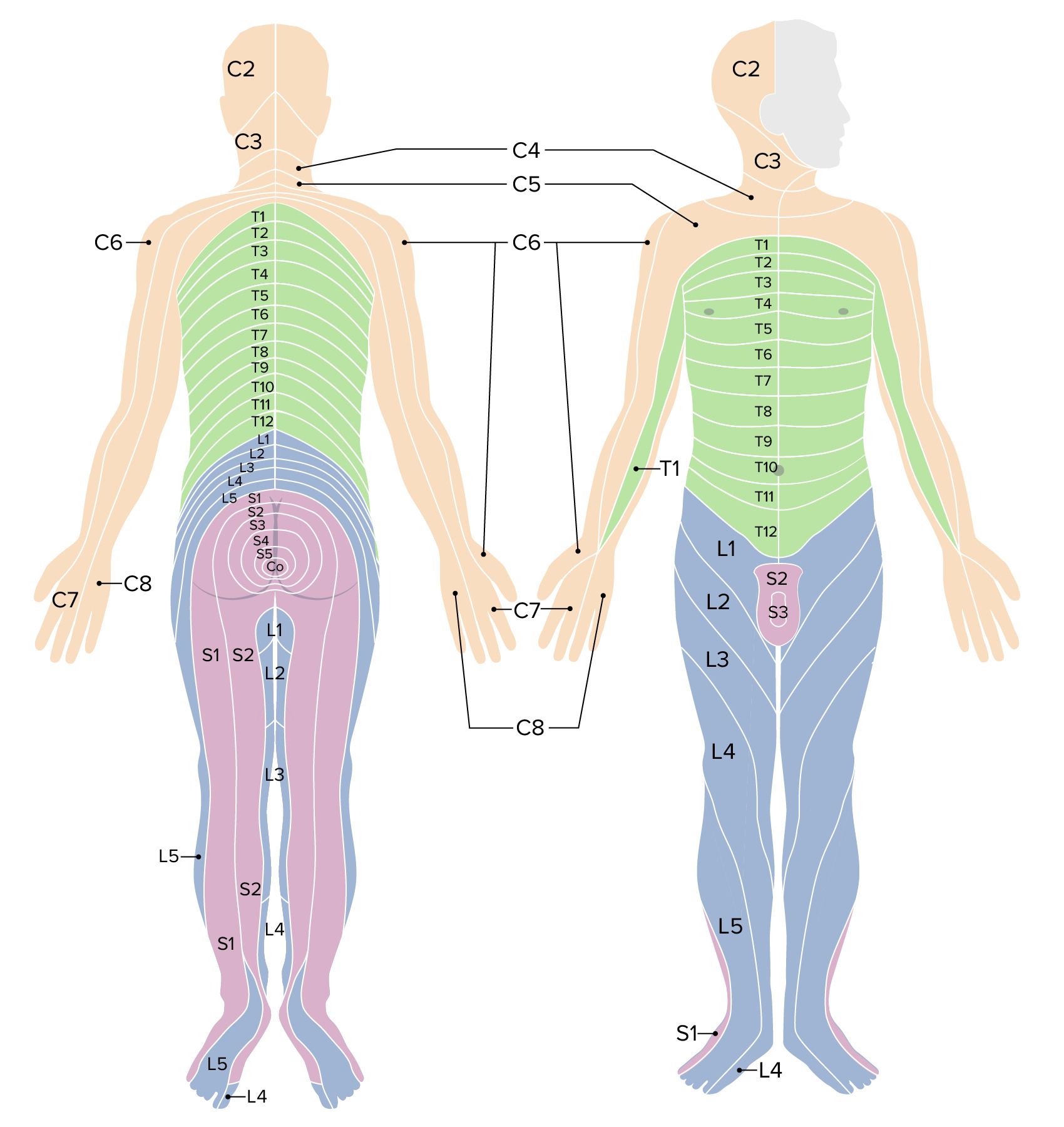
Spinal Cord Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge

Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerves

Spinal Cord Column Spinal Cord Injury Information Pages

Spinal Nerve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
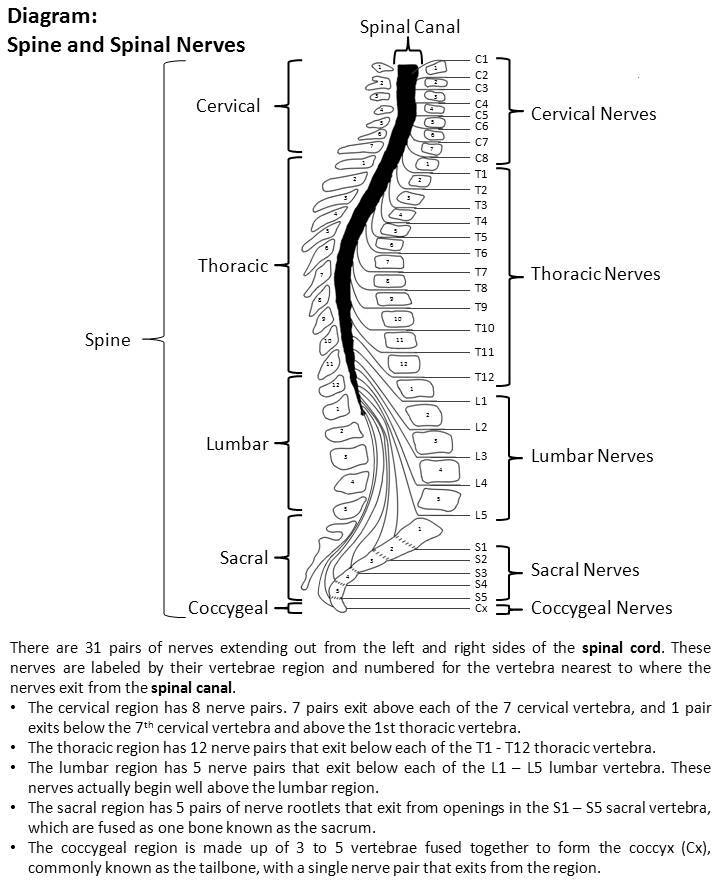
What Does The Spinal Cord Do Spinal Cord Injury Model System Uab

Spinal Nerve Definition Function Diagram Number Facts Britannica
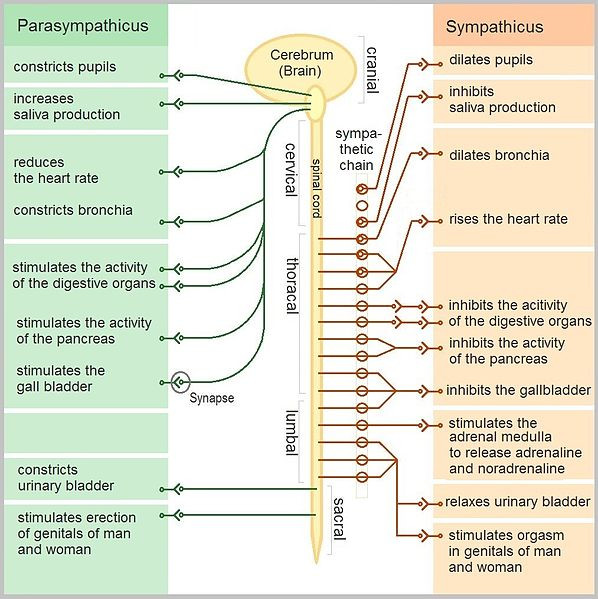
12 6f Function And Physiology Of The Spinal Nerves Medicine Libretexts

What Are The 31 Pairs Of Spinal Nerves Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


Comments
Post a Comment